Geo configuration (GitLab Omnibus)
Note: This is the documentation for the Omnibus GitLab packages. For installations from source, follow the Geo nodes configuration for installations from source guide.
Configuring a new secondary node
Note: This is the final step in setting up a secondary Geo node. Stages of the setup process must be completed in the documented order. Before attempting the steps in this stage, complete all prior stages.
The basic steps of configuring a secondary node are to replicate required configurations between the primary and the secondaries; to configure a tracking database on each secondary; and to start GitLab on the secondary node.
You are encouraged to first read through all the steps before executing them in your testing/production environment.
Notes:
- Do not setup any custom authentication in the secondary nodes, this will be handled by the primary node.
- Any change that requires access to the Admin Area needs to be done in the primary node, as the secondary node is a read-only replica.
Step 1. Manually replicate secret GitLab values
GitLab stores a number of secret values in the /etc/gitlab/gitlab-secrets.json
file which must match between the primary and secondary nodes. Until there is
a means of automatically replicating these between nodes (see issue gitlab-org/gitlab-ee#3789),
they must be manually replicated to the secondary.
-
SSH into the primary node, and execute the command below:
sudo cat /etc/gitlab/gitlab-secrets.jsonThis will display the secrets that need to be replicated, in JSON format.
-
SSH into the secondary node and login as the
rootuser:sudo -i -
Make a backup of any existing secrets:
mv /etc/gitlab/gitlab-secrets.json /etc/gitlab/gitlab-secrets.json.`date +%F` -
Copy
/etc/gitlab/gitlab-secrets.jsonfrom the primary to the secondary, or copy-and-paste the file contents between nodes:sudo editor /etc/gitlab/gitlab-secrets.json # paste the output of the `cat` command you ran on the primary # save and exit -
Ensure the file permissions are correct:
chown root:root /etc/gitlab/gitlab-secrets.json chmod 0600 /etc/gitlab/gitlab-secrets.json -
Reconfigure the secondary node for the change to take effect:
gitlab-ctl reconfigure gitlab-ctl restart
Step 2. Manually replicate primary SSH host keys
GitLab integrates with the system-installed SSH daemon, designating a user (typically named git) through which all access requests are handled.
In a Disaster Recovery situation, GitLab system administrators will promote a secondary Geo replica to a primary and they can update the DNS records for the primary domain to point to the secondary to prevent the need to update all references to the primary domain to the secondary domain, like changing Git remotes and API URLs.
This will cause all SSH requests to the newly promoted primary node from failing due to SSH host key mismatch. To prevent this, the primary SSH host keys must be manually replicated to the secondary node.
-
SSH into the secondary node and login as the
rootuser:sudo -i -
Make a backup of any existing SSH host keys:
find /etc/ssh -iname ssh_host_* -exec cp {} {}.backup.`date +%F` \; -
SSH into the primary node, and execute the command below:
sudo find /etc/ssh -iname ssh_host_* -not -iname '*.pub' For each file in that list replace the file from the primary node to the same location on your secondary node.
-
On your secondary node, ensure the file permissions are correct:
chown root:root /etc/ssh/ssh_host_* chmod 0600 /etc/ssh/ssh_host_* -
Regenerate the public keys from the private keys:
find /etc/ssh -iname ssh_host_* -not -iname '*.backup*' -exec sh -c 'ssh-keygen -y -f "{}" > "{}.pub"' \; -
Restart sshd:
service ssh restart
Step 3. Add the secondary GitLab node
- Visit the primary node's Admin Area ➔ Geo Nodes
(
/admin/geo_nodes) in your browser. - Add the secondary node by providing its full URL. Do NOT check the box 'This is a primary node'.
- Optionally, choose which namespaces should be replicated by the secondary node. Leave blank to replicate all. Read more in selective replication.
- Click the Add node button.
-
SSH into your GitLab secondary server and restart the services:
gitlab-ctl restartCheck if there are any common issue with your Geo setup by running:
gitlab-rake gitlab:geo:check -
SSH into your GitLab primary server and login as root to verify the secondary is reachable or there are any common issue with your Geo setup:
gitlab-rake gitlab:geo:check
Once added to the admin panel and restarted, the secondary will automatically start replicating missing data from the primary in a process known as backfill. Meanwhile, the primary node will start to notify the secondary of any changes, so that the secondary can act on those notifications immediately.
Make sure the secondary instance is running and accessible. You can login to the secondary node with the same credentials as used in the primary.
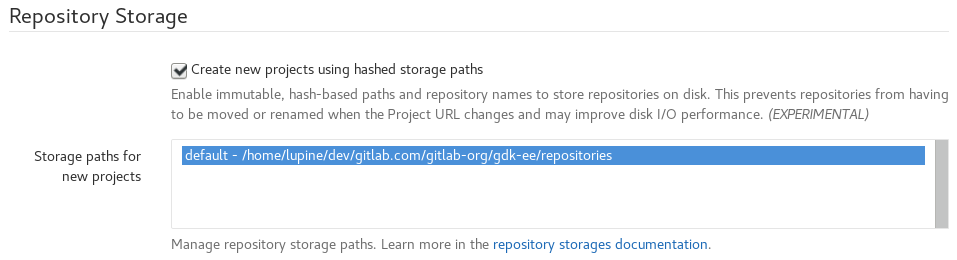
Step 4. (Optional) Enabling hashed storage (from GitLab 10.0)
CAUTION: Warning: Hashed storage is in Beta. It is not considered production-ready. See Hashed Storage for more detail, and for the latest updates, check infrastructure issue gitlab-com/infrastructure#2821.
Using hashed storage significantly improves Geo replication - project and group renames no longer require synchronization between nodes.
- Visit the primary node's Admin Area ➔ Settings
(
/admin/application_settings) in your browser -
In the
Repository Storagessection, checkCreate new projects using hashed storage paths:
Step 5. (Optional) Configuring the secondary to trust the primary
You can safely skip this step if your primary uses a CA-issued HTTPS certificate.
If your primary is using a self-signed certificate for HTTPS support, you will need to add that certificate to the secondary's trust store. Retrieve the certificate from the primary and follow these instructions on the secondary.
Step 6. Enable Git access over HTTP/HTTPS
Geo synchronizes repositories over HTTP/HTTPS, and therefore requires this clone
method to be enabled. Navigate to Admin Area ➔ Settings
(/admin/application_settings) on the primary node, and set
Enabled Git access protocols to Both SSH and HTTP(S) or Only HTTP(S).
Step 7. Verify proper functioning of the secondary node
Congratulations! Your secondary geo node is now configured!
You can login to the secondary node with the same credentials you used on the
primary. Visit the secondary node's Admin Area ➔ Geo Nodes
(/admin/geo_nodes) in your browser to check if it's correctly identified as a
secondary Geo node and if Geo is enabled.
The initial replication, or 'backfill', will probably still be in progress. You can monitor the synchronization process on each geo node from the primary node's Geo Nodes dashboard in your browser.
If your installation isn't working properly, check the troubleshooting document.
The two most obvious issues that can become apparent in the dashboard are:
- Database replication not working well
- Instance to instance notification not working. In that case, it can be
something of the following:
- You are using a custom certificate or custom CA (see the troubleshooting document)
- The instance is firewalled (check your firewall rules)
Please note that disabling a secondary node will stop the sync process.
Please note that if git_data_dirs is customized on the primary for multiple
repository shards you must duplicate the same configuration on the secondary.
Point your users to the "Using a Geo Server" guide.
Currently, this is what is synced:
- Git repositories
- Wikis
- LFS objects
- Issues, merge requests, snippets, and comment attachments
- Users, groups, and project avatars
Selective synchronization
Geo supports selective synchronization, which allows admins to choose which projects should be synchronized by secondary nodes.
It is important to note that selective synchronization does not:
- Restrict permissions from secondary nodes.
- Hide project metadata from secondary nodes.
- Since Geo currently relies on PostgreSQL replication, all project metadata gets replicated to secondary nodes, but repositories that have not been selected will be empty.
- Reduce the number of events generated for the Geo event log
- The primary generates events as long as any secondaries are present. Selective synchronization restrictions are implemented on the secondaries, not the primary.
A subset of projects can be chosen, either by group or by storage shard. The former is ideal for replicating data belonging to a subset of users, while the latter is more suited to progressively rolling out Geo to a large GitLab instance.
Upgrading Geo
See the updating the Geo nodes document.
Troubleshooting
See the troubleshooting document.